Breast Reconstruction-1 Breast Reconstruction-2 Breast Reconstruction-3 Breast Reconstruction-4
Breast reconstruction surgery aims to create a new tumor in the breast with modern restoration of the shape and the creation of a new nipple, strengthening the self-confidence of the woman who has undergone this type of amputation surgery. Many breast reconstruction techniques are described, including tissue augmentation, microsurgical tissue transfer (free flap) and fat transplantation. The time of rehabilitation is done in consultation with the specialized surgeon-oncologist and depending on the state of health of the patient.
Rehabilitation with silicone implants
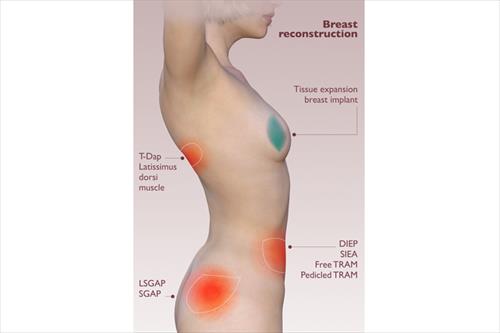
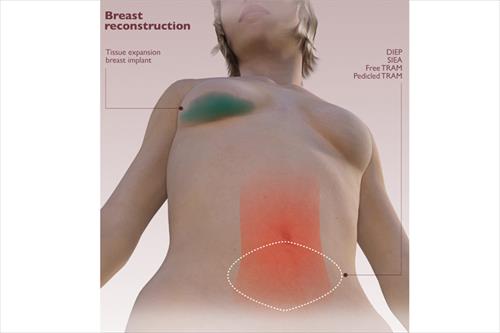
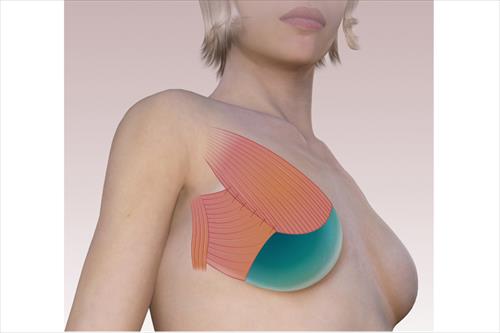
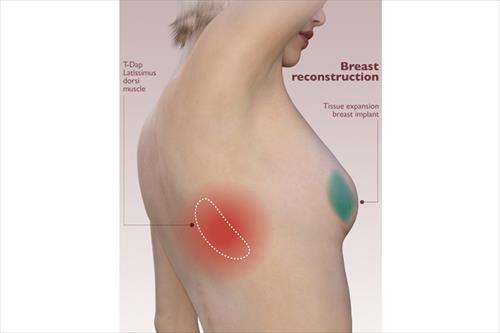
It is the most common way of restoration and is done with similar implants that are used to increase breast volume. Due to the small amount of skin in the area, the operation most often begins with the placement of skin dilators. Dermal dilators are synthetic implants that are gradually filled with saline to relax the skin and increase its amount in the area. In this way they will create a new place where the permanent silicone insert will be placed. This technique ensures the greatest possible viability of the silicone implant and minimizes complications.
Restoration with tissue flaps
It is the alternative proposal for breast reconstruction. In this case a part of the patient's own body is used to increase the volume of her breast. The piece of tissue used can be from the back, abdomen or buttocks and includes a combination of fat and muscle skin. If the piece comes from the abdomen, the operation is combined with abdominoplasty. The recovery time of such an operation is longer, while it can not be done in very thin or obese women.
After rehabilitation surgery
Women who choose to have their breasts surgically repaired should be aware that their recovery time is generally longer than an operation to correct or reduce it. The majority of patients can return to work within a period of six weeks. However, the total recovery time can be more than a year and can even be extended if additional surgeries are needed.









 Login
Login Forgotten password
Forgotten password